HashMap
在之前的学习中我们也提到过HashMap的一些特点,这里再简单地总结下:
非线程安全的实现方式
作为一种通用实现,它的key和value都可以是null
迭代器实现了fast-fail机制,即在迭代过程中如果发生了并发修改操作,会抛出异常
数据存储
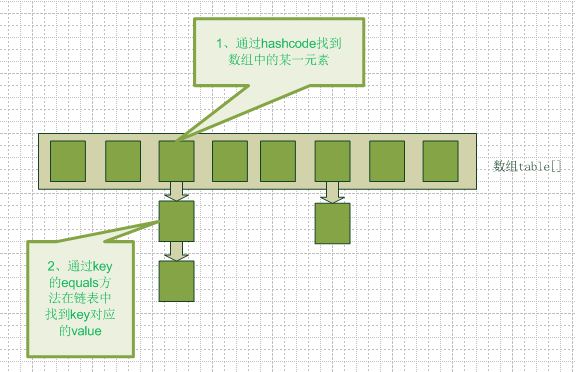
我们都知道map中的数据是以键值对的形式存储的,那么在hashMap中,具体存储的数据格式是怎么样的,当我们执行put或者get操作时,底层到底是如何实现的呢?一起先来看看HashMap的存储结构,如下图所示,hashMap事实上是数组和链表的组合体,每个键值对被封装成entry存储在这个结构中,每个entry除了提供的key和value之外,还有个很重要的元素是hash,它的值是由key经过hash计算得来的.
PUT操作
put操作的源码如下所示:
首先先根据提供的key值计算相应的hash值, 这个hash值决定了这个键值对会被存储在map中的哪个bucket中,即决定了图中数组的下标;而hash值的计算是根据Key的hashCode方法计算后取其高位16位得到,注意这里如果提供的key为null值,默认得到的哈希值为0,即key为null的键值对会被默认存储于0号桶中
得到hash, key, value后(暂时忽略onlyIfAbsent以及evict参数,它对hashMap的影响不是本质性的),会调用 putVal方法,这个方法首先检查数组的长度,如果为空或者数组长度为0,则进入resize操作(resize操作的细节请参见resize一章).紧接着就会根据提供的hash值计算这个键值对所在的bucket的位置(在代码中为变量i的值),这里分两种情况
如果数组的当前索引位置上没有元素,那么可以直接把这个元素放到数组的这个索引位置上
如果数组的当前索引位置上有元素,说明当前键值对的哈希值和Map中存储的另一键值对的哈希值发生了碰撞,在这种情况下,hashMap引入了链表的结构来进行存储。通过遍历链表上的元素,并通过key.equals()方法来比较当前的键值对和链表上的元素是否相等,如果相等那么直接进行替换,如果直到链表尾部也没有找到相等的元素,那么就在链表尾部插入新的键值对
在完成元素的插入操作后,hashMap还会进行一次判断,比较当前map里存储的元素个数和预先设定的threshold值,这个阈值是由数组初始化长度和loadFactor相乘得来 ,如果超过这个阈值,说明当前Map中的负载已经较高,那么就进行一次resize操作,将数组的长度扩大一倍
除此之外,hashMap还做了一些优化,比如当某个bucket的链表超过一定数量时,它会把链表转化成树来存储,当少于一定数量时,又会转化成链表来存储;另外,通过modCount这个参数来实现了迭代器的fast-fail机制.
|
|
GET操作
理解了put操作的原理后,再来理解get操作就非常简单了.
首先还是根据提供的key值计算相应的hash,计算的方法和put时使用的方法是一样的,否则可能会造成取不到值了
得到相应的hash值之后,相当于就知道这个元素所在的bucket的位置了,这个bucket在前面讲过,就是个链表结构,所以剩下要做的就是遍历这个链表,取出相应的值即可. 在遍历链表的时候,比较的是提供的key值和链表中的key值是否相等,通过key.equals()方法来判断,如果相等,说明找到了相应的值,直接返回;如果直到链表结尾都没有找到相等的元素,那么直接返回null即可.
|
|
RESIZE操作
resize操作是在map中存储的键值对个数超过预先设置的阈值时对hashMap进行扩容的实现,预设的阈值由capacity和load_factor两个参数共同决定, capacity决定了数组的初始长度,而load_factory决定了当数组的负载达到多少的时候,进入resize操作.
首先判断旧的数组长度,如果长度不为0,则直接将capacity和threshold扩大为原来的两倍
如果旧数组长度为0, 说明这是个初始化操作, 初始化的数组长度保存于threshold中
如果capacity和threshold都为0,新的数组长度和阈值均采用默认值
在计算好新的数组长度和阈值之后,要做的就是遍历原来的元素并将迁移到现在的数组中. 注意这里的每个数组元素可能都是一个链表,所以每次遍历的是一个链表,而不是一个数组元素。在遍历的时候,还要注意的是这里将hash和原来的数组长度按位并操作,如果得到的结果为0,说明这个元素在新的数组中还是应该存储在原来的索引位置上,如果得到的值不是0,说明这个键值对在新的数组中应该放在另外的位置,这个位置就是原先位置偏移oldCap个索引的位置.
|
|

